L-Arginine is a naturally occurring amino acid found in many foods. Here you should know how L– Arginine benefits to your health. It plays an important role in the building of protein, which helps the body repair and grow muscle. It also helps in the formation of nitric oxide, which helps to open blood vessels. L-arginine also stimulates the body to produce insulin and growth hormone, as well as other chemicals. It is often used for circulatory purposes and is needed for the formation of proteins.
Some of the uses for l-arginine include: Erectile dysfunction, High blood pressure, NEC (Necrotizing Enterocolitis) is a serious illness affecting premature infants. These are just a few of the conditions in which it is used. There are many other conditions that it is used for. However, none of these conditions are well supported by science.
This article reviews How L– Arginine benefits to your health, its side-effects and applications of L-arginine supplements.
What is L-arginine?
L-arginine is an amino acid that is essential or optional to proteins. Unlike other amino acids, essential amino acids can’t be made by the body. Instead, they need to be supplied through food.
It is classified as a semi-essential amino acid or a conditionally essential amino acid, meaning it only becomes necessary under certain conditions and circumstances (e.g., pregnancy, early infancy, severe illness, or trauma). It is needed to synthesize nitric oxide (a signaling molecule) which is essential for many body functions and processes (e.g. blood flow regulation, mitochondria functioning, cellular communication, etc.). It also acts as a precursor for other amino acids (glutamate, proline and creatine) which are needed for the growth and maintenance of the immune system.
L-arginine plays a vital role in the functioning of cells and organs, and a deficiency of this amino acid can lead to serious health problems. There are many ways for the body to produce arginine. You can get arginine from the citrulline amino acid your body breaks down, or you can get it from eating enough protein.
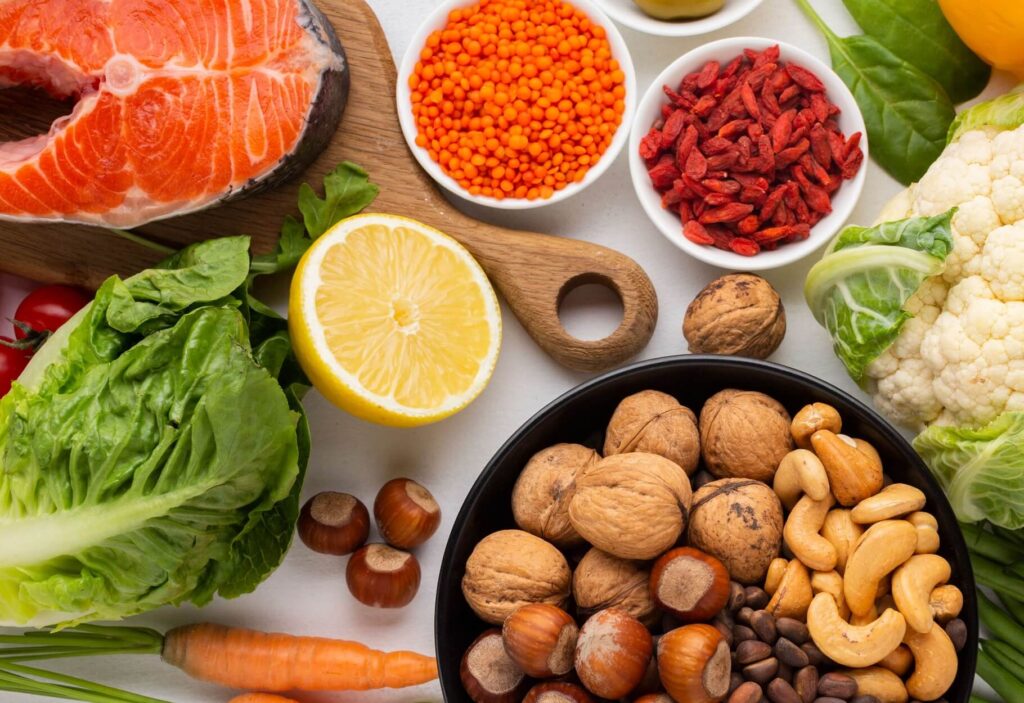

What foods contain L-arginine?
L-arginine is naturally present in foods high in protein, such as:
- Fish (salmon, haddock).
- Meat (turkey, chicken, and red meat).
- Legumes (such as chickpeas and soybeans).
- Whole grains (oats, brown rice).
- Nuts and seeds (pumpkin seeds, cashews).
- Dairy goods (cheese, yogurt, and milk).
It has been estimated that 4-6 grams of L-arginine are consumed through food each day. L-arginine can also be acquired by taking supplements. These supplements are widely accessible and can be purchased online, in supplement stores, and in powder, liquid, capsule, and tablet form.
How L-arginine benefits to your health?
1. Nutrition Therapy:
L-arginine has been studied to help reduce the time it takes for wounds to heal after surgery, and to help cancer patients build lean body mass when used in combination with omega-3 fatty acids and nucleotides.
2. Athletic performance enhancement:
L-arginine may increase exercise performance by increasing nitric oxide levels in your body, which helps improve blood flow and a constant flow of oxygen to your muscles, according to several studies. In one small study, researchers found that athletes who took supplements had significantly higher nitric oxide levels and were able to exercise for longer.
3. Erectile dysfunction:
L-arginine supplements have been studied in men with ED. It is thought that L-arginine increases nitric oxide, which relaxes the muscles surrounding the blood vessels supplying the penis. This causes the penis’s blood vessels to widen and blood flow to increase, which may help maintain an erection.
4. Blood pressure regulation:
L-arginine contains nitric oxide, which helps regulate blood pressure and relax the blood vessels. Its supplements may help those with high blood pressure to lower their systolic blood pressure (the highest number in the blood) and their diastolic (lowest) blood pressure (the lowest number in the blood). Studies have shown that supplementing with L-arginine can significantly lower adults’ systolic or diastolic blood pressure readings by 5.4 millimeters per millimeters (mm/Hg) and 3.1 millimeters per milliliters (mmHg) respectively.
5. Management of critical illness:
L-arginine is an amino acid that your body needs when your immune system is weak due to infection or trauma. When your body’s physiological need for L-arginine increases dramatically, your body can’t provide enough L-arginine. Therefore, you need to supplement your body with L-arginine from external sources. When your body needs too much L-arginine during or after surgery or illness, it can lead to serious side effects, such as decreased blood flow and a weakened immune system. Adding L-arginine to your diet may help reduce the negative consequences of trauma or severe illness.
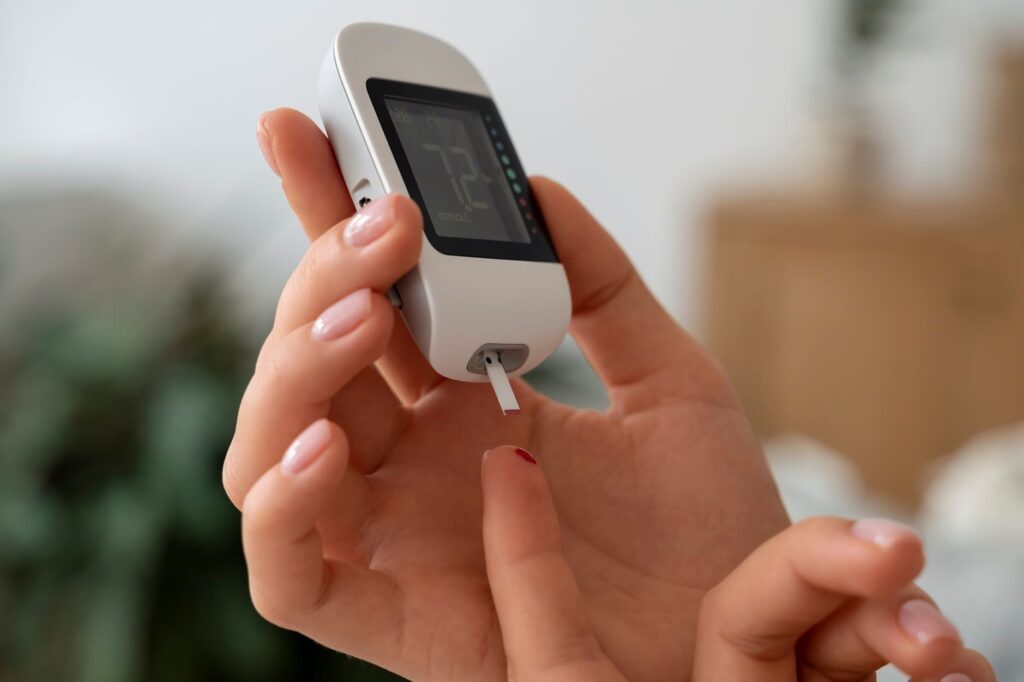

6. Blood sugar regulation:
L-arginine has not been extensively studied, but there is some evidence that it may improve insulin sensitivity in people with diabetes and improve glucose metabolism. Since nitric oxide must be made, L-arginine is needed. Nitric oxide is an essential part of how cells function and how your body responds to the hormone insulin. Insulin carries blood sugar from the blood into your cells and uses it for energy. Boosting nitric oxide availability may improve the performance of insulin-secreting cells and help your body better use blood sugar.
7. Treating pregnancy complications:
Pregnancy complications that may benefit from L-arginine include preeclampsia (high blood pressure) and gestational hypertension (high blood pressure during pregnancy). Pre-eclampsia occurs when the blood pressure and urine protein levels are too high for the baby to survive. When given intravenously, it can reduce blood pressure in pregnant women who are at risk for preeclampsia. However, only medical professionals are allowed to administer these IV products. It is not known if L-arginine can be ingested.
8. Improving blood flow:
L-arginine has been shown to improve blood vessel health and improve blood flow in certain groups of people. However, there is a lot of mixed evidence, and many people think that it is useless. Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) is a narrowing of the blood vessels that reduces the flow of blood to the limbs. For patients with PAD, oral or intravenous L-arginine can increase blood flow up to 8 weeks. However, it does not help increase walking distance or speed for up to 6 months.
9. Other potential benefits:
- Treating and preventing preeclampsia – Many studies have shown that treatment with L-arginine during pregnancy may help prevent and treat this condition.
- Correcting hereditary disorders of urea synthesis – The urea cycle in the body uses arginine to create urea, a substance found in urine.
- Easing inflammation of the digestive tract in premature infants – According to a study, L-arginine may aid in the prevention of necrotizing enterocolitis (a serious condition that affects premature infants).
- Treating peripheral arterial disease – People who have peripheral arterial disease may benefit from L-arginine because of its effects on widening blood vessels.
- Chest pain (angina) – L-arginine supplementation appears to lessen angina symptoms, increase exercise tolerance, and enhance quality of life.
- High blood pressure during pregnancy – Taking L-arginine intravenously during pregnancy can lower blood pressure.
- L-arginine may also help with a range of other health issues. However, further research is needed to determine if it can help those with respiratory illnesses breathe more easily, heal wounds faster, and reduce anxiety more effectively.
Therefore, it is important to consult with your doctor before taking any dietary supplements. It is important to read and understand the claims made by the manufacturer before using any product. Because dietary supplements are not regulated by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), they may contain higher or lower dosages than those listed on the label.
Possibly Ineffective for:
• Tuberculosis – L-arginine oral supplementation appears to have no effect on tuberculosis symptoms or infection clearance when combined with standard therapy.
• Elevated cholesterol – L-arginine taken orally has no effect on cholesterol levels.
• Chronic kidney disease (CKD) – In the majority of CKD patients, receiving L-arginine intravenously or orally does not improve kidney function.
• Cardiomyopathy – L-arginine taken orally does not appear to help prevent heart attacks. Furthermore, it doesn’t appear to be any use in the aftermath of a heart attack. In fact, there is worry that L-arginine may be detrimental for those who have recently suffered a heart attack. If you have recently experienced a heart attack, avoid taking L-arginine.
What are possible side effects?
It is safe and well-tolerated when used as a supplement for at least one year. However, large doses can cause bloating, nausea and diarrhea, as well as stomach pain. People with Asthma, Cirrhosis, Kidney Disease, Low Blood Pressure, and an Inherited Deficiency (Guanidinoacetate Methyltransferase Deficiency) Affects the Metabolism of this Amino Acid and may have adverse effects, although the safety profile is supported by scientific evidence. Higher doses may worsen heartburn or ulcers or digestive upset caused by medication because it increases stomach acid. L-Arginine may worsen symptoms in patients with Herpes.
L-arginine has been proven to be safe in many groups of people, including elderly people and pregnant women. L-arginine are sometimes given to children in clinical settings and are considered safe when prescribed in proper doses. However, children should always be given arginine supplements under the supervision of their doctor. Your doctor should always approve and supervise the use of supplements while you are pregnant or breastfeeding woman.
What are risks and complications?
For some populations, L-arginine poses some potentially serious risks. These may include:
- Long-term supplementation may result in kidney damage.
- Potential to stimulate tumor growth; interactions with certain drugs, such as sildenafil (Viagra), and blood pressure medications.
- Elevated risk of death following a heart attack.
- Decreased blood pressure.
The majority of studies suggest that, in low doses, L-arginine is safe for most people. However, because the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) does not control the safety or effectiveness of supplements, it is important to choose a company that does independent research. You can purchase supplements online, but like any drug or supplement, there is always a chance that the risks will outweigh the benefits. Therefore, it is recommended that you consult with a doctor or a dietitian before using L-arginine.
What are interaction with other medicines?
L-arginine may interact with medications used for erectile dysfunction, high blood pressure, or diabetes, among other medications. Do not take it if you are diabetic or have heart disease. Some studies suggest that chronic L-arginine supplementation may decrease insulin sensitivity, but other studies have not found any effect or increased insulin sensitivity. As with many other supplements, L-arginine has not been studied for safety in pregnant, nursing women, young, old women, those with medical conditions, or those taking medication.
Dosage and Preparation:
There is no “right” dose for you. Factors such as age, gender and medical history can influence the dosage that works best for you. Some studies have looked at different doses to see how they affect different conditions. For example, a 2–6 g dose given 3 times a day for up to 1 month was found to help with chest pain. Another study found that a 5 g daily dose was effective in treating erectile dysfunction, and a 4–24 g daily dose was used in high blood pressure studies for up to 24 weeks. Talk to your health care provider for specific guidance.

What are natural ways to get enough L-arginine?
L-arginine is difficult to consume, which is one of the main benefits of consuming it through diet. Eating too much of it can lead to some of the following adverse effects: On the other hand, you may not be able to get enough of it from food to meet your needs. Therefore, it is important to consult with your doctor before making any dietary changes.
The best sources of natural L-arginine are foods rich in protein. For some people, animal proteins such as red meat, chicken and turkey breast meat, pork loin and dairy products are their main sources. If you are a vegetarian or vegan, you may want to consider changing your diet to include more protein-rich foods. Your doctor or dietitian may be able to recommend a meal plan to help you increase your natural intake of L-arginine before taking supplements.
Conclusion:
L-arginine is an amino acid that your body needs in order to function. You can get it from your diet by eating some animal and plant-based protein. You can also get it as a supplement by eating fish, red meats, poultry, soya, grains, beans, dairy products, and more. Benefits of L-arginine supplements include: Improve heart health, lower blood pressure, lower blood sugar, Improve athletic performance, oral and topically administered supplements are available. However, some supplements may cause gastrointestinal problems and may interact with drugs. Therefore, it is recommended that you consult a doctor before taking any supplements. Consuming a healthy diet is the best way to get natural.
FAQ
What are the benefits of taking L-arginine supplements?
L-arginine supplements are often used because they can increase nitric oxide production, which can improve blood flow. This improved blood flow can help people with conditions such as erectile dysfunction by promoting better circulation. L-arginine is also thought to promote cardiovascular health by relaxing blood vessels and lowering blood pressure. Some athletes also take supplements because they believe they improve exercise performance by increasing the supply of nutrients and oxygen to muscles. However, it’s important to always talk to a healthcare professional before adding any supplements to your routine. Everyone’s response is different.
Does L-arginine help with erectile dysfunction?
As nitric oxide is a chemical that relaxes blood vessels, it is thought to play a role in improving erectile function. Nitric oxide can improve blood flow to your genitals, which is essential for achieving and sustaining an erection. Some studies suggest that supplementing with L-arginine may help people with mild-to-moderate erectile dysfunction (MTFD). However, it’s important to remember that this effect can vary from person to person, so it’s best to consult with your healthcare provider to determine the best course of treatment for your erectile dysfunction.
How does L-arginine improve exercise performance?
L-arginine helps improve exercise performance by increasing nitric oxide production. Nitric oxide is a chemical that helps dilate your blood vessels. When your blood vessels are dilated, your blood flow increases. As your blood vessels dilate, your muscles get more oxygen and nutrients. This can help increase your exercise tolerance and reduce fatigue. While there are some studies that suggest that exercise performance can be improved by taking certain supplements, individual reactions may vary. Therefore, it is best to consult with a healthcare professional before adding L-arginine to your fitness routine.
Are there any side effects of L-arginine supplementation?
Most people who supplement with L-arginine experience only mild side effects when taken in the correct amounts. However, some people may experience gastrointestinal side effects such as bloating, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. On rare occasions, higher doses of arginine may cause more serious side effects such as: Low blood pressure, Allergy, and Worsening asthma symptoms. It is important for people who are considering arginine supplementation to consult their healthcare provider to determine the correct arginine dosage and to evaluate the risks associated with arginine for their medical history.
Can L-arginine promote heart health?
L-arginine can help improve heart health by increasing nitric oxide production, which relaxes and dilates blood vessels, increasing blood flow. Improved blood circulation may help lower blood pressure and improve overall cardiovascular function. While there are some studies that suggest benefits, it’s important to talk to your doctor about the proper use and potential risks for your individual heart health.
Reference used:
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/l-arginine
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/drugs/22536-l-arginine
https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/l-arginine#what-it-is
https://www.verywellhealth.com/using-l-arginine-for-health-88322